Contraceptives and things to know about them.
Wednesday, January 22, 2025
Did you know there are over 7 different ways to prevent pregnancy and protect your health?
Contraceptives are more than just birth control, they are about choice, control, and confidence.
Learn the options in simple terms!!
Contraceptives, or birth control methods, help prevent pregnancy and sometimes protect against infections. They give people control over when or if they want to have children.
CONDOMS
Condoms are thin coverings worn during sex. They stop sperm from reaching an egg, preventing pregnancy. They also protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), including HIV.
They include:
- Male condoms
Worn on the penis, they're easy to find and simple to use.
- Female condoms
Worn inside the vagina, they provide a similar barrier.
Condoms are a great choice if you want both pregnancy prevention and protection from STIs.
BIRTH CONTROL PILLS
These pills contain hormones that stop ovulation (the release of an egg). Without an egg, pregnancy cannot happen.
They need to be taken daily, ideally at the same time each day.
There are two main types:
combination pills (contain estrogen and progestin) and progestin-only pills (often called the "mini-pill").
Benefits include regular periods, less cramping, and reduced acne. However, they don’t protect against STIs.
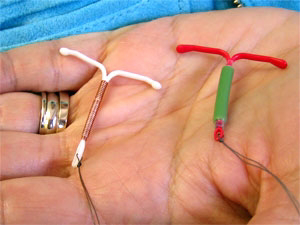
ITRAUTERINE DEVICES (IUD)
IUDs are small devices placed inside the uterus by a doctor. They’re one of the most effective forms of birth control.
- Copper IUDs
Non-hormonal, they prevent sperm from fertilizing an egg. They can last up to 10 years.
- Hormonal IUDs
These release hormones to prevent pregnancy and can last 3-6 years.
IUDs are long-term and low-maintenance but require a healthcare provider for insertion and removal.
IUDs can cause discomfort during insertion, irregular bleeding, and, in rare cases, infection or displacement.
IMPLANTS
A tiny rod is placed under the skin of your upper arm by a doctor. It releases hormones that prevent pregnancy for up to 3 years. It is a set-it-and-forget-it method but does not protect against STIs.
Implant contraceptives can cause side effects like irregular bleeding, weight changes, or mood swings and require a healthcare provider for insertion and removal.
EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTIVES (PLAN B OR THE MORNING AFTER PILL)
If unprotected sex happens, this pill can be taken within 72 hours to prevent pregnancy. It is not for regular use and works best the sooner you take it. It does not protect against STIs.
INJECTION (DEPO-PROVERA)
This is a hormonal shot given by a doctor every three months. It is highly effective if you stick to the schedule but does not protect against STIs
Depo-Provera can cause irregular bleeding, weight gain, mood changes, and delayed fertility return.
STERILIZATION
For those who don’t want children in the future:
- For women
Tubal ligation (“getting your tubes tied”) blocks the fallopian tubes.
- For men
Vasectomy cuts the tubes that carry sperm
These are permanent methods, so think carefully before choosing them.
NATURAL METHODS
- Fertility awareness
Tracking your menstrual cycle to avoid sex during fertile days.
- Withdrawal method
Pulling out before ejaculation.
These methods require discipline and are not as reliable as others.
CHOOSING THE RIGHT METHOD
Each method has pros and cons. When choosing, consider:
- How effective it is.
- Whether it protects against STIs.
- Your health and lifestyle.
- Whether you want children in the future.